|
Differentiability
Text The function f is differentiable at a point (x0,y0, z0) if
lim(x,y,z) --> (x0,y0,z0) |f(x,y,z) - L(x,y,z)|/d((x,y,z), (x0,y0,z0)) = 0
where d((x,y,z), (x0,y0,z0)) = √[(x-x0)^2 + (y - y0)^2 + (z - z0)^2] is the distance from (x,y,z) to (x0,y0,z0) and L(x, y, z) is the equation for the tangent plane to the function f(x, y, z) at the point (x0, y0, z0).

An alternative definition is that a function f is differentiable at a point p in its domain if there exist functions fx, fy, and fz such that
limh --> 0 |f(p+h) - f(p) - fx(p)h1 - fy(p)h2 - fz(p)h3|/|h| = 0
where h = (h1,h2,h3). This condition can be written in terms of epsilons and deltas as well. We say that f is differentiable at p if for any ε > 0 there exists a &delta > 0 such that
|f(p+h) - f(p) - fx(p)h1 - fy(p)h2 - fz(p)h3|/|h| < ε
or
-ε|h| + fx(p)h1 + fy(p)h2 + fz(p)h3 < (f(p+h) - f(p)) < ε|h| + fx(p)h1 + fy(p)h2 + fz(p)h3
whenever |h| < &delta. This definition of differentiabilty is similar in form to the definition of continuity. Recall that in the geometrical interpretation of continuity the challenge was to find a small enough &delta-disc domain at p such that the surface over the domain would lie between two horizontal plates a distance ε above and below f(p). In the geometrical interpretation of differentiability, as seen in the inequality above, the challenge is to find a &delta-sphere domain, centered at p, that is small enough so that the surface over the domain lies between two spherical hypercones, where the value of ε determines the slope of the hypercones.
An easier way to visualize this is to consider a slice of the function. For this slice surface, it must be true that the portion of the surface lying over a slice of the spherical domain must lie between two conic slices of the hypercone. This is a way of reducing the problem of differentiability in three dimensions to a problem in two dimensions, which we can understand more easily. The function of three variables will be differentiable at a point if it is differentiable for every slice through that point.

Demos
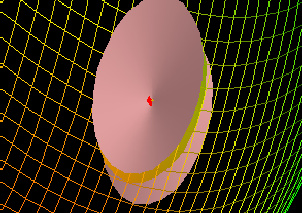
Geometrical Interpretation of Differentiability

| 
|
The first step in this demo is to choose a function f(x, y, z) and some point P at which to test the differentiability of f. Next, choose some small ε that will determine the hypercones which must be the bounds of the function for some &delta in order for the function to be differentiable. Now, examine each slice through point P by rotating the slice plane in the "Plane Orientation" window (do this by rotating the normal to the plane). If you find some orientation for which the slice of the function passes through the slice cones, try making &delta smaller. If you cannot find any &delta small enough, then the function is not differentiable. If you can always find a small enough &delta for every slice, then the function is differentiable. 
|
Exercises Test whether each function below is differentiable at the specified point:
- f(x, y, z) = x2 + y2 + z2, P = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
- f(x, y, z) = |z|, P = (0, 0, 0)
- f(x, y, z) = |z|, P = (0, 0, 0.1)
- f(x, y, z) = |x| + |y| + |z|, P = (0, 0, 0)
- f(x, y, z) = |x3| + |y3| + |z3|, P = (0, 0, 0)
|