allahallahA pattern can be thought of as existing on a net or grid that supports the underlying structure. Every pattern has a basic "building block" shape which, when repeated on the net, fitting together in various ways, produces an infinite field of pattern. There are five of these basic building block shapes (called unit cell shapes):
allahallah(1) parallelogram, (2) rectangle, (3) centered rectangle, (4) square, and (5) hexagonal.
The first step in classification is to identify what net block the pattern is using:
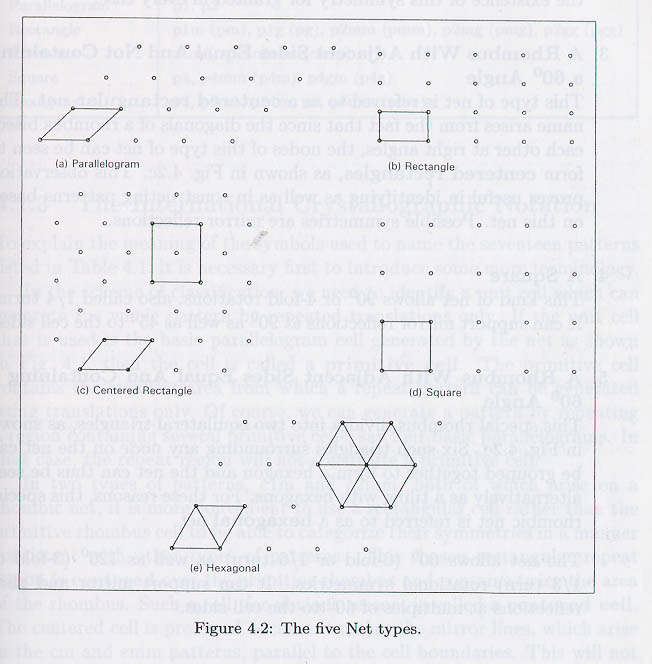
Scanned from Symmetries of Islamic Geometrical Patterns
allahallah Symmetric patterns are classified based on the unit cell shape. Each different kind of pattern is given a standardized abbreviation. The numbers and letters of the abbreviation are a short-hand way of saying what kinds of symmetrical actions are performed on the unit cell shape in order to produce the pattern. This table lists the 17 different pattern types, and an explanation of the notation follows it.