|
Hessian Matrices
Text The Hessian matrix H of a function f(x,y,z) is defined as the 3 * 3 matrix with rows [fxx, fxy, fxz], [fyx, fyy, fyz], and [fzx, fzy, fzz].
For twice continuously differentiable functions, a critical point will be a maximum or minimum if and only if the solutions λ to det(H - λI) = 0 are all positive.
Demos
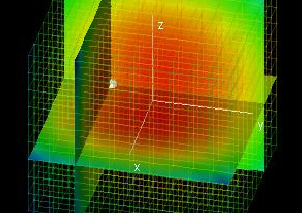
Hessian Matrices

| 
|
This lab displays the graph of a function f(x, y, z) and the graph of the polynomial given by det(H - λI) as a function of λ. H is the Hessian matrix for the point (x0, y0, z0), which you can choose using the hotspots. If the point chosen is a critical point, it will be a maximum if and only if the graph of the polynomial intersects the x-axis for positive values of λ only. 
|
Exercises 1. Are the solutions to det(H - λI) = 0 all positive at the point (0, 0, 0) for f(x, y, z) = x2 + y2 + z2? Why should this answer be expected (consider the geometric meaning of x2 + y2 + z2)?
2. Are the solutions to det(H - λI) = 0 all positive at the point (0, 0, 0) for f(x, y, z) = x2 + y2 - z2?
3. Explain why in the two dimensional case, a set of all positive solutions λ to det(H - λI) = 0 implies that fxxfyy - fxyfyx > 0.
|